Malaria: The Lethal Bite
Mosquitoes are known carriers of life-threatening, if not deadly, diseases. One of these dreaded diseases that a mosquito is capable of infecting a healthy human and making him or her sick is the parasitic Malaria. This is a mosquito-borne disease caused by microorganisms called protists. It has been estimated to have historically killed billions of humans in the whole world.
Mosquitoes need to feed on blood in order for them to breed or reproduce. In this process, the protists that cause malaria are transmitted through the mosquito’s saliva into the human victim’s circulatory system. [pullquote]Only female Anopheles mosquitos are capable of transmitting such protists or parasites. [/pullquote]Even more alarming with this information is that Anopheles mosquitos can be found and are living in 48 U.S. states.
Malaria is also the most commonly imported disease in the United States with an estimate of about 1,000 cases coming in the country. A dangerous characteristic of this disease is that when parasites from a female anopheles mosquito infect a healthy individual, it becomes asymptomatic until such time that they have taken over the body. This disease can also transmitted or spread even to those people who never leave their homes. One more thing, NO ONE is immune to this disease.

Malaria, U S Army medical researchers take part in World Ma…—US Army Africa (Flickr.com)
The parasites are single-celled animals that hide in Red Blood Cells and are stored up inside the gut of the Female Anopheles mosquito. After about 10 days inside the mosquito’s gut, they become eel-like creatures that when introduced into the human bloodstream through mosquito bites will find its way to the liver and will live inside a single cell. Six days after, the parasites can multiply in up to 20,000 times and are ready to make the attack.
When the malaria parasites make their move to take over the human body, the natural defenses block them from doing so. The White Blood Cells of our body’s defense system engulfs these parasites to hinder them from further infesting the body. However, malaria parasites escape the White Blood Cells by burrowing themselves inside the Red Blood Cells. Once inside the healthy blood cell, they feed on hemoglobin and multiply again in huge numbers getting ready for their final attack.
When they make for the final attack, the parasites are just too many that the body’s defense cannot fight them well because they are being outnumbered. Once this happens, the human victims will feel the symptoms of malaria like fever and headache. These and other symptoms are commonly the result of toxins that are produced when the body fights against the parasites. Quinine is one of the only drugs that can kill and eliminate these parasites once it has invaded the human body.
All over the world, malaria attacks affect an estimate of about 500 million people and kill nearly 2 million of those victims. Most of these cases happen in developing countries.
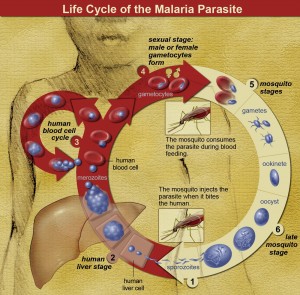
Malaria cycle image: National Institutes of Health (NIH)
Filed under: Mosquito Bites Treatment
Like this post? Subscribe to my RSS feed and get loads more!



Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.